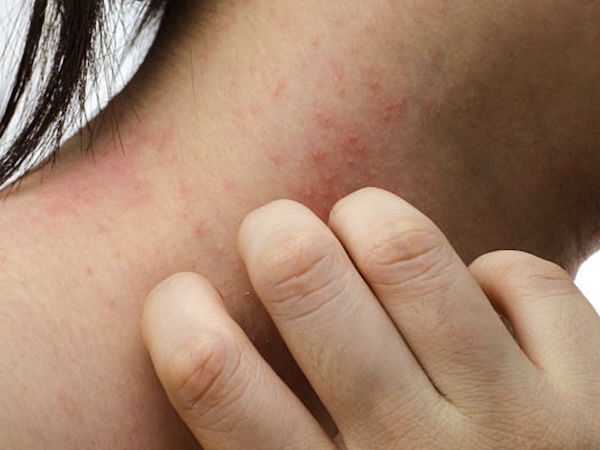
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that causes the rapid buildup of skin cells, leading to scaly, itchy and inflamed patches on the skin. It most commonly appears on the elbows, knees, scalp and lower back, but it can affect any part of the body.
This condition is non-contagious, but it can significantly impact a person's physical comfort, emotional well-being and self-confidence. Psoriasis tends to flare up periodically and may range from mild to severe.
What causes Psoriasis?
Psoriasis occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, speeding up their life cycle and causing abnormal skin cell buildup. While the exact cause isn’t fully understood, several triggers and risk factors are known:
- Genetics – A family history of psoriasis increases the risk.
- Stress – Emotional or physical stress can trigger flare-ups.
- Infections – Strep throat and other infections may worsen symptoms.
- Weather – Cold, dry climates tend to aggravate psoriasis.
- Injury to the skin – Cuts, burns or insect bites can trigger new patches.
- Medications – Some drugs, including lithium or beta-blockers, may trigger symptoms.
- Lifestyle factors such as alcohol consumption, smoking and an unhealthy diet may also contribute to flare-ups.
What are the symptoms of Psoriasis?
Psoriasis presents differently for each person, but common symptoms include:
- Thick, red patches of skin with silver or white scales
- Itching, burning or soreness in the affected areas
- Dry, cracked skin that may bleed
- Thickened or ridged nails
- Joint pain or stiffness in some cases (psoriatic arthritis)
How is Psoriasis diagnosed?
- Visual examination of the skin, nails and scalp by a dermatologist
- Medical history evaluation, including family history and known triggers
- Skin biopsy, in rare cases, to rule out other skin conditions
What are the conventional treatments for Psoriasis?
Conventional treatment for psoriasis aims to reduce inflammation, slow skin cell turnover, and manage triggers. Common treatments include:
- Topical therapies – Corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, coal tar or moisturizers
- Phototherapy (light therapy) – Controlled exposure to UVB light
- Systemic medications – Immunosuppressants or oral drugs for severe cases
- Biologic injections – Targeted therapies that block specific immune responses
While these methods can manage symptoms, they may come with side effects or provide only temporary relief, especially if underlying causes are not addressed.
What lifestyle changes help manage Psoriasis?
Certain lifestyle changes can greatly improve the effectiveness of treatment and reduce flare-ups:
- Use gentle, fragrance-free skincare products
- Moisturize regularly to prevent dryness and cracking
- Avoid known triggers like stress, smoking and alcohol
- Follow an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables and omega-3 fatty acids
- Practice stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation or deep breathing
- Stay hydrated and maintain a healthy weight
Is there an ayurvedic treatment for Psoriasis?
Yes, Ayurveda offers a holistic and natural approach to treating psoriasis by focusing on internal detoxification, immune balance, and skin nourishment. In Ayurvedic terms, psoriasis is often linked to an imbalance in Vata and Kapha doshas, along with impurities in the blood (Rakta Dushti).
Ayurvedic treatment for Psoriasis Include:
- Panchakarma Therapy - A powerful detoxification process that includes Virechana (purgation) and Basti (medicated enema) to eliminate toxins and balance doshas.
- Takradhara - A soothing treatment where medicated buttermilk is poured over the forehead to calm stress and reduce inflammation.
- Herbal Oils and Pastes - External application of Neem oil, Karanja oil or Manjistha paste helps soothe itching, reduce scales and heal the skin naturally.
- Internal Herbal Remedies - Herbs like Neem, Turmeric (Haridra), Khadir, Guduchi and Manjistha purify the blood, reduce inflammation and boost immunity.
- Dietary Guidelines (Pathya-Apathya) - An anti-psoriatic Ayurvedic diet avoids dairy, sour and fermented foods, while encouraging light, warm and detoxifying meals.
- Lifestyle Modifications - Daily self-care routines (Dinacharya), stress management and seasonal cleanses help maintain doshic balance and prevent recurrence.